The boat "Meteor" is a river passenger ship. It is a hydrofoil vessel. It was developed by the domestic shipbuilder Rostislav Alekseev.
History of "Meteor"
The Meteor boat dates back to 1959. It was then that the first such experimental ship was launched. Sea trials took place for almost three weeks. Within their framework, the very first boat "Meteor" covered the distance from Gorky to Feodosia. The ship was built at a factory called "Krasnoye Sormovo".
In Feodosia "Meteor" wintered. He set off on his return journey only in the spring of 1960. This time it took him five days to sail from Feodosia to Gorky. The tests were considered successful by all participants.
Mass production

The characteristics of the ship suited everyone, so already in 1961 it was put into mass production. It was established at the Gorky shipyard, which was located in Zelenodolsk. Over 30 years, more than 400 motor ships from this series have been produced here.
At the same time, the design bureau did not stand still. New, improved versions are constantly being developed. So, the Nizhny Novgorod designers proposed to make the "Meteor" on hydrofoils. In this case, imported engines and air conditioners were used. The history of this ship ended only in 2007, when the line was finally dismantled, rebuilt for a new class of motor ships.
Inventor of Meteor
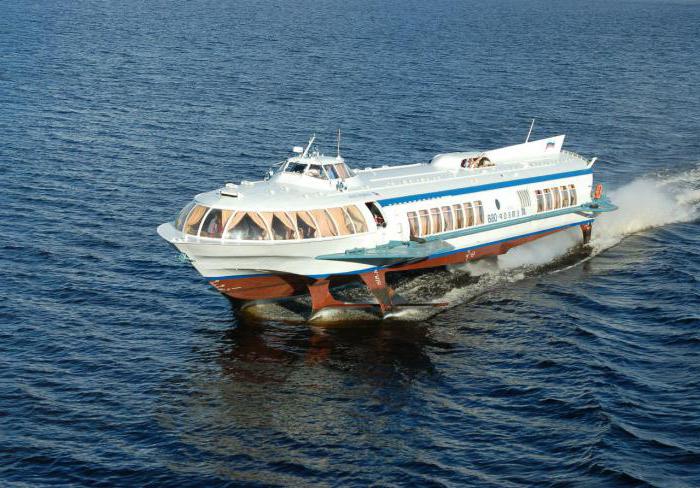

By right, the shipbuilder Rostislav Alekseev is considered the creator of the Meteor boat. In addition to air-winged ships, his merit is the appearance in our country of ekranoplans (high-speed vehicles flying in the area of the aerodynamic screen) and ekranoplanes (using the screen effect for flights).
Alekseev was born in the Chernigov province back in 1916. In 1933 he moved with his family to Gorky, where he developed a successful working career. He graduated from the Industrial Institute, defended his thesis on hydrofoil gliders. He began working as a shipbuilding engineer.
During the Great Patriotic War he was allocated resources and people to create hydrofoil combat boats. The leadership of the Soviet Navy believed in his idea. True, their creation was delayed, so they did not have time to take part directly in hostilities. But the resulting models convinced skeptics of the possibility of implementing this project.
Working on "Meteor"

"Meteor" on hydrofoils a group of scientists began to develop under the leadership of Alekseev. Initially, it received the symbolic name "Rocket".
The world community became aware of this project in 1957. The ship was presented at the International Festival of Youth and Students, which was held in Moscow. After that, active shipbuilding began. In addition to the boat "Meteor", the technical characteristics of which turned out to be impressive, projects were created under the names "Petrel", "Volga", "Voskhod", "Sputnik" and "Comet".
In the 60s, Alekseev created an ekranoplan for the navy and a separate project for the airborne troops. If the flight altitude of the first was only a few meters, then the second could rise to a height comparable to airplanes - up to seven and a half kilometers.
In the 1970s, Alekseev received an order for the Orlyonok airborne landing craft. In 1979, for the first time in the world, an ekranolet ship was adopted by the navy as an official combat unit. Alekseev himself regularly tested his vehicles. In January 1980, while testing a new model of a passenger civil ekranolet, which was supposed to be completed by the Moscow Olympics, it crashed. Alekseev survived, but received numerous injuries. He was urgently hospitalized. Doctors fought for his life, two operations were performed. But on February 9, he still died. He was 63 years old.
Hydrofoils

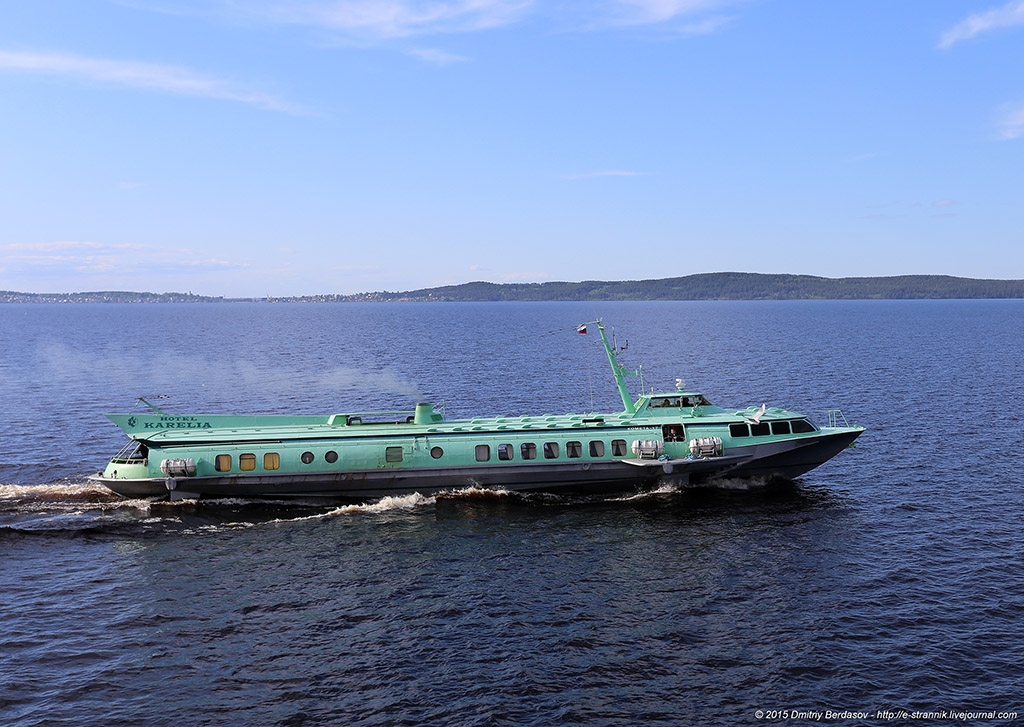
"Meteor" on hydrofoils is a vivid example of ships of this class. It has hydrofoils under the hull.
Among the advantages of such aircraft are high speed of movement, low resistance when moving on wings, insensitivity to rolling and high cross-country ability.
However, they also have significant drawbacks. Their main disadvantage is low efficiency, especially compared to low-speed displacement ships, while they start having problems when the water is rough. In addition, they are not adapted to unequipped parking lots, and for movement they need powerful and compact engines at the same time.
Description of Meteor

"Meteor" is a hydrofoil ship, which is designed for high-speed transportation of passengers. He runs on diesel, he is single-deck. Used exclusively during daylight hours on navigable rivers. It is also possible to move through freshwater reservoirs and lakes, but only in areas with a predominantly temperate climate. It is controlled remotely, its movement is controlled directly from the wheelhouse.
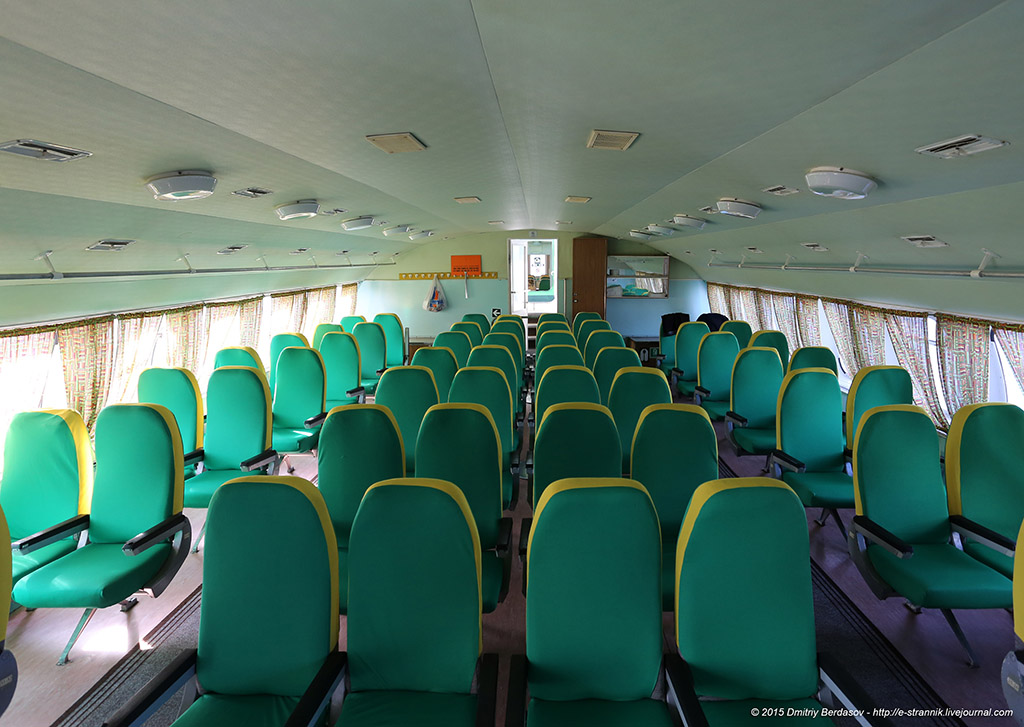
Passengers are in three cabins with comfortable and soft chairs. They are located in the bow, middle and stern parts of the vessel. A total of 114 passengers fit. Movement between parts of the vessel is carried out through the deck, from which doors lead to the toilet, utility rooms and engine room. In the middle salon there is even a buffet for those who want to refresh themselves.
The wing device includes load-bearing wings and flaps. They are fixed on the sides and bottom racks.
The main engines are two diesel ones. At the same time, a combined unit consisting of a diesel engine with a capacity of up to 12 horsepower is required to service the power plant. The mechanical plant is controlled from the wheelhouse and the engine room.
Power supply of the ship
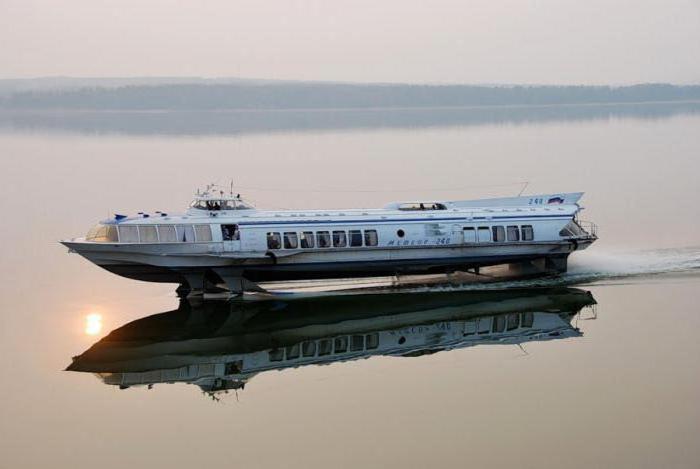

"Meteor" - a ship for which two running generators are considered the main source of electricity direct current. Their power is one kilowatt at a stable and normal voltage.
There is also an automatic machine for the simultaneous operation of batteries and a generator. There is also an auxiliary generator that is used directly to power consumers.
Specifications
The passenger ship "Meteor" has enviable technical characteristics. The empty displacement is 36.4 tons, and the total displacement is 53.4 tons.
The length of the vessel is 34.6 meters, the width is nine and a half meters with a hydrofoil span. Parking height - 5.63 meters, while on the wings - 6.78 meters.
Draft also differs when standing and running on the wings. In the first case, 2.35 meters, in the second - 1.2 meters. Power varies from 1,800 to 2,200 horsepower. The speed of the Meteor boat can reach a maximum of 77 kilometers per hour, as a rule, it is operated at a speed of 60-65 kilometers per hour. The vessel can sail autonomously for about 600 kilometers.
One of the disadvantages of the Meteor is fuel consumption. Initially, it was about 225 liters per hour, but thanks to the use of new modern engines, today it can be significantly reduced - by about 50 liters of fuel per hour.
The crew is small - only three people.
Distribution countries "Meteor"
Currently, the mass production of "Meteors" has been discontinued, so new ships of this type no longer appear. But their operation continues today. In particular, they are used by the river fleet of the Russian Federation, they are also common in other countries.
Until now, they can be seen in Hungary, Greece, Vietnam, Italy, Egypt, China, Kazakhstan, Poland, Romania, Slovakia and the Czech Republic.
These river hydrofoils were actively used in Bulgaria until about 1990, in Latvia until 1988, in Ukraine until 2000, in the Netherlands until 2004, and in Germany until 2008. Now in these countries they have been replaced by more modern vehicles.
Safe travel
Fascinating river trips and walks are organized today using the Meteor. Safety on the ship for passengers is guaranteed by a special control system and regular thorough maintenance of all devices and mechanisms. Therefore, we can say with confidence that, going on a voyage on the Meteor, you do not risk anything.
You can ride this river boat in different parts of the country. For example, excursions from St. Petersburg to Peterhof and back are very popular today. The ship sets off on a journey through the picturesque places of the Neva, tourists can enjoy amazing beauties Northern Palmyra. Moreover, everything is done for the convenience of people, it is not even necessary to waste time in line at the box office, it is enough to purchase a ticket online.
This high-speed river boat will delight you with a smooth ride, which is provided by powerful and reliable modern engines. On board each ship there are systems of radio navigation control, communications and necessarily air conditioning.
In three comfortable cabins, passengers are protected from any vagaries of nature. In soft armchairs that take the form of a tourist, they can fully relax, have a bite to eat, using the folding wooden tables hidden in the armrests.
Between the chairs there are also round tables made of natural wood, which are much larger. They will come in handy if you are traveling in a friendly company on the way.
Service for tourists
It should be noted that today these vehicles are mainly used for tourist purposes. Therefore, they organize the most comfortable pastime. Service is given great attention.
The companies organizing such river cruises provide a full range of services, providing for everything that a vacationer may need. For example, tourist services, which include not only the transportation and accommodation of passengers, but also the organization of good nutrition, exciting entertainment programs and educational excursions.
Using a convenient form for ordering tickets for these river boats on the Internet, you will not only save time, but also fully enjoy an unforgettable trip along the great rivers of Russia.
A lot of fascinating and useful facts are devoted to the Meteor ship, which will not only expand your horizons, but also make the trip on this ship even more exciting.
Most of them are collected in a book called "Winged Vessels of Russia", which combines all the most interesting things about this unusual type of water transport.
For example, one of the captains of the ship "Meteor", which moved on hydrofoils, was the famous Hero of the Soviet Union, a participant in the Great Patriotic War, Mikhail Devyatayev. Fighting against the Nazi invaders, he was captured, but managed to free himself and even hijack an enemy bomber.
A successful escape was carried out in February 1945 from a concentration camp located in Germany.
And in 1960, the new ship was shown to the head of the Soviet Union, Nikita Sergeevich Khrushchev. The famous aircraft designer Andrei Tupolev, who was present at the same time, was so impressed by what he saw that he even asked the main developer, Alekseev, for permission to jointly manage the ship.
Today, the Meteor has been replaced by the passenger ship Lena, which is also produced at the shipyard in Zelenodolsk. In the future, this project is being developed at a shipyard located in Khabarovsk. It is capable of covering a distance of 650 kilometers. At the same time, it develops average speed up to 70 kilometers per hour. Can accommodate 100 passengers or 50 with VIP accommodation. And the crew is only 5 people.
Traveling around our country every day you discover something new. So today, on a cruise in Petrozavodsk, I discovered just such a curiosity. These are hydrofoil ships "Kometa" and "Meteor". Since I was not prepared to meet such vessels, the Meteor practically did not get into the frame, because I thought that they were the same. From Petrozavodsk "Meteors" and "Kometa" operate flights along Lake Onega to Kizhi, Velikaya Guba and Shala. The fare, for example, to Kizhi is 1375 rubles one way. Pleasure is not cheap.
1. "Kometa" - a series of sea (the first in this class) passenger ships on hydrofoils. The motor ship was developed in 1961 at the Central Design Bureau for Hydrofoils named after I. R. E. Alekseeva. Serially produced in 1964-1981 at the Feodosia shipbuilding plant "More" (a total of 86 Komets were built, including 34 for export) and in 1962-1992 at the Poti shipyard (project 342 ME, 39 ships).

2. Displacement 41.2 t (empty), 58.3 t (full), length 35.1 m, width 11.0 m, height 7.8 m (when running on wings), draft 3.6 m (when parked) , 1.7 m (when running on wings).

3. The ship is equipped with 2 diesel engines M-401A, 1 auxiliary diesel generator-compressor-pump. Power 2200 hp, propeller 2 propellers, travel speed 60 km/h (maximum), 55-57 km/h or 30 knots (operational).
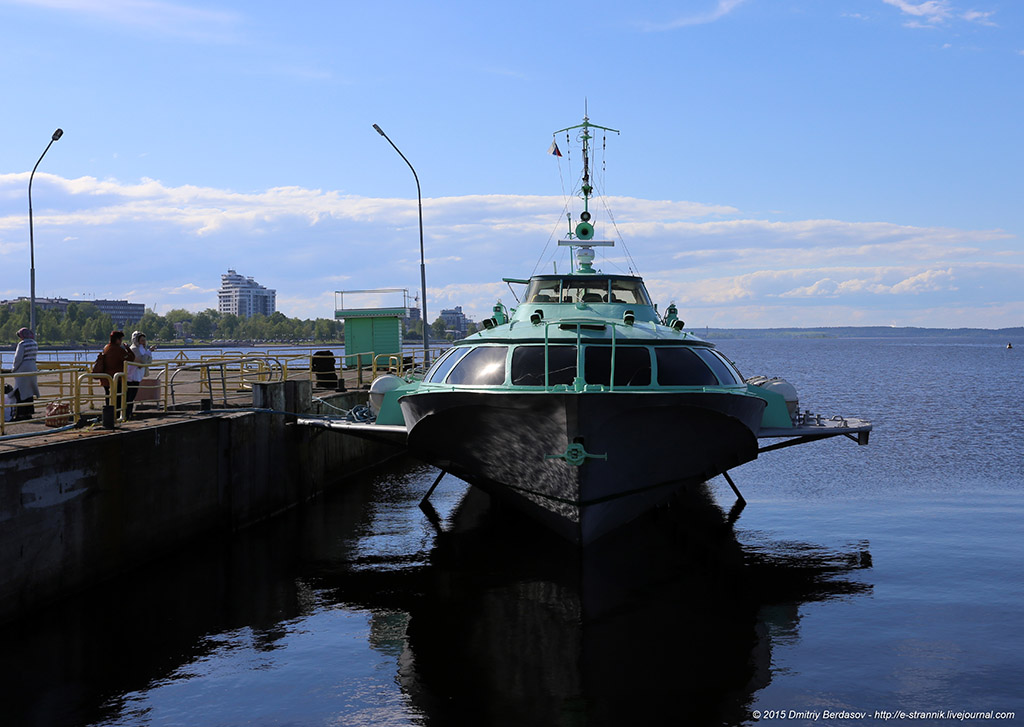

4. Crew 5 people, passenger capacity up to 120 people (depending on modification). Passengers are accommodated in three cabins equipped with soft seats: bow, middle and stern. The passenger compartment resembles the cabin of an aircraft, because even the seats are of an aircraft type.

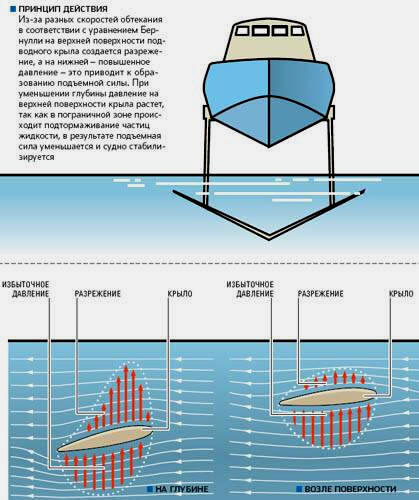
5. In the parking lot and when moving at low speed, the hydrofoil is kept on the water due to the force of Archimedes, like an ordinary displacement vessel. At high speed, due to the lift created by these wings, the ship rises above the water. At the same time, the area of contact with water is significantly reduced, and, consequently, the hydrodynamic and frontal resistance of water, which allows you to develop a higher speed.

6. "Meteor", project 342E hydrofoil river passenger ship, developed by Rostislav Alekseev. Produced from 1961 to 1991 at the Zelenodolsk shipbuilding plant named after. A. M. Gorky. In total, more than 400 ships of this series were built.

7. And this photo is a bonus. Here is such a sunset today on Lake Onega.

My next post will be about the city of Petrozavodsk. As they say, Stay tuned.
Motor ship "Rocket" was intended for high-speed river passenger transportation on suburban and local lines, up to 500 km long, with entry into reservoirs Length - 27 m. Width - 5 m. Draft afloat - 1.8 m. m. The power of the power plant is 850 hp. Speed - 60 km / h. Passenger capacity - 64 people.
The first attempts to create a hydrofoil were made at the end of the 19th century. In 1897, a Russian subject, Charles de Lambert, who lived in France, built and tested a small hydrofoil on the Seine. However, the power of the steam engine used on this ship as an engine was not enough to develop the speed necessary for the ship's hull to rise above the water.

More successful were the experiments of the Italian inventor Enrico Forlanini. He has been experimenting with hydrofoil models since 1898. In 1906, the full-size experimental vessel he created reached a speed of 42.5 miles per hour (68 km / h) during tests on Lake Lago Majore. This boat had multi-tiered wings like a bookcase.
In the 30s, the German engineer Hans von Schertel, with a large group of scientists and practitioners, worked very seriously on the idea of a high-speed hydrofoil vessel. By that time, suitable materials for the construction of the hull and quite suitable powerful engines had appeared. Only one thing did not exist - the optimal form of a hydrofoil.
Shertel tested models of the most unthinkable shapes, but nothing worked. The ship did not move. In some cases, he lacked stability when moving on the water, in others, the wing lift was insufficient and the ship did not rise above the water. The golden mean was never found, although the hydrofoil system created by Shertel found application. And yet, the full practical implementation of the hydrofoil idea was not given to foreign researchers.
Around the same years, a student of the shipbuilding department of the Gorky Polytechnic Institute, Rostislav Alekseev, was interested in an article in the collection of scientific works of TsAGI. The article considered the behavior of an aircraft wing in some dense flow, for example, in water. The author argued: the stronger the flow, the faster the hydrodynamic forces arise, providing the lifting force of the wing.
The young man was captured by the idea - to force those hydrodynamic forces to serve, which just did not allow ships to increase speed, made water transport slow. In a word, he decided to turn the enemy into a friend.
And turned!
In the autumn of the forty-first year, Rostislav Alekseev, a graduate of the institute, defended his thesis “Hydrofoil glider”. The State Examination Board heard about a ship it didn't know yet world history shipbuilding. The diploma work was recognized as corresponding to the level of the PhD thesis.
Salon "Rockets"
In Alekseev's project, the effect of a low-submerged hydrofoil (Alekseev's effect) was used. Hydrofoil Alekseev consists of two main horizontal bearing planes - one in front and one behind. The dihedral angle at the convergence is either small or absent, the weight distribution is approximately equal between the front and rear planes. A submerged hydrofoil, rising to the surface, gradually loses its lift, and at a depth approximately equal to the length of the wing chord, the lift approaches zero. It is due to this effect that the submerged wing is not able to fully come to the surface. At the same time, a relatively small hydroplaning (sliding on the surface of the water) wing liner is used to help with the “winging out”, and also does not allow the vessel to return to the displacement mode. These fender liners are located in close proximity to the front pillars and are installed so that they touch the surface of the water while underway, while the wings are submerged to a depth approximately equal to the length of their chord. The whole system was first tested on a small boat, which was driven by a 77-horsepower car engine.
After defending his diploma, R. E. Alekseev received a referral to the Gorky Krasnoye Sormovo plant, to the technical control department: the young shipbuilder became the controller of the Quality Control Department for receiving tanks - the main product of the plant. It was military time.
On his first boat, R. E. Alekseev went to Moscow in 1946. It was accepted by interested organizations, specialists got acquainted with the vessel. The idea of a hydrofoil ship had its first supporters not only in Gorky, but also in Moscow. A tiny team of the laboratory set about the technical design of the world's first hydrofoil vessel, codenamed "Rocket".
The first passenger hydrofoil under the same name entered service in 1957. The first ship in the series, Rocket-1, was built at the Krasnoye Sormovo shipyard. Rocket-1 made its first flight on August 25, 1957. During this flight, the distance of 420 kilometers from Gorky to Kazan was covered in seven hours. There were thirty passengers on board.

Serial production of "Rockets" was launched at the Feodosia shipyard "More". From 1959 to 1976, 389 Rockets were built, including 32 for export. High-speed diesel engines were supplied by the Leningrad plant Zvezda.
"Rockets" were very popular, their name became a household name and often all ships of this type are called that. A trip on the "Rocket" to some picturesque bay was one of the favorite, although not cheap (ticket prices for such ships significantly exceeded the prices for commuter trains for the same distance), types of family recreation on the river.
In Nizhny Novgorod, "Rockets" were used in daily suburban transportation, as well as excursion ships.
In Moscow, the first "Rocket" (namely, "Rocket-1") appeared during the VI International Festival of Youth and Students in the summer of 1957. The “Rocket” was brought to the capital by the chief designer of the ship, Rostislav Evgenievich Alekseev, and personally demonstrated it to Khrushchev.
On the basis of Alekseev's developments, a large number of commercial hydrofoil ships were built in Russia: "Rocket", "Strela", "Sputnik", "Meteor", "Comet", "Cyclone", "Petrel", "Voskhod". Military ships were also built, including the largest ship of this class in the world, the Butterfly, preceded by the Bee, Turya and Locust.
Mass exploitation of "Rockets" in Moscow was carried out from the beginning of the 1960s until 2006. There were also routes in the Moscow region: from MSRV to Chiverevo, Aksakovo, Tishkovo, Chernaya River.
There was also a fire modification "Rocket-P" with two fire nozzles and water and air-foam protection systems. Range of "shooting" - 90 m. Water supply - 800 cubic meters. m/hour.
In a short time, hydrofoils have become one of the most popular modes of transport. Speed, seaworthiness, comfort, high efficiency allowed winged ships to successfully compete with other modes of transport. The Soviet Union had the largest fleet of cruise ships in the world. In addition to the "Rocket", other types of civilian hydrofoil motor ships were built in the USSR. By 1985, more than 1,000 Volga boats, hundreds of Raketa motor ships, dozens of Kometa, Meteor and Belarus motor ships were used on the country's waterways. In our country, hydrofoils annually transported more than 20 million passengers on regular lines. Soviet cruise ships were successfully exported to many countries, including the USA, Germany, France, Italy and Great Britain.
Since 2007, the gradual restoration of the Rockets began in Moscow. So, for example, in 2009, four "Rockets" were operated: 102 (VIP-salon, not used in regular flights), 185, 191 (former number 244) and 246.
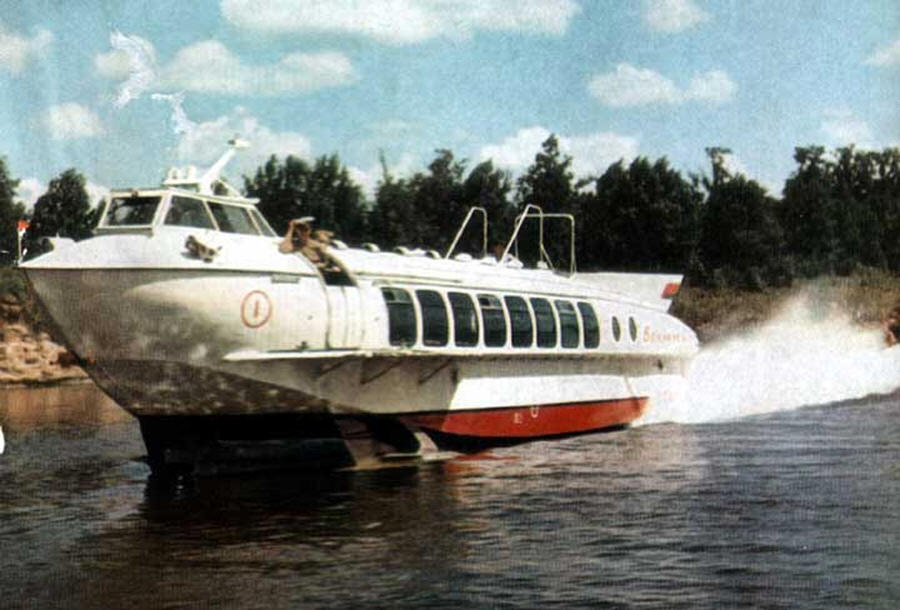

The ship "Belarus" was distinguished by the fact that it had a very small draft: afloat - 0.91, while on wings - 0.3 meters. For comparison: the same parameters for the ship "Rocket" - 1.8 and 1.1 meters. "Belarus" served suburban and local river lines up to 320 kilometers long. The vessel took on board 40 passengers and, with an operating power of 600 horsepower, develops a speed of 65 kilometers per hour.
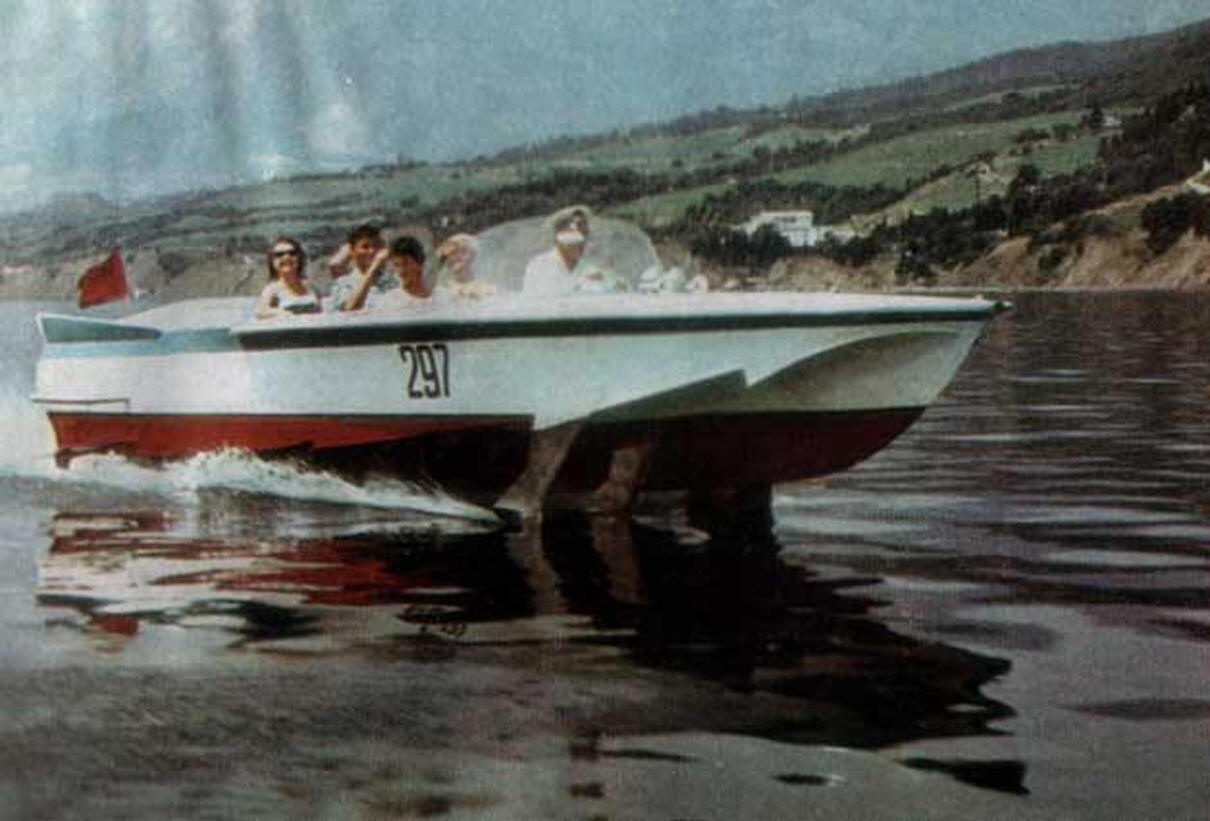

The boat "Volga" was intended for walks, water tourism and business and traveling purposes. It can be used on coastal sea lines, as well as on rivers, lakes and reservoirs up to 180 km long. Length - 8.5 m. Width - 2.1 m. Draft afloat - 0.85 m. Draft with wings - 0.55 m. Speed - 60 km / h. Power - 70 hp Passengers - 6 people.
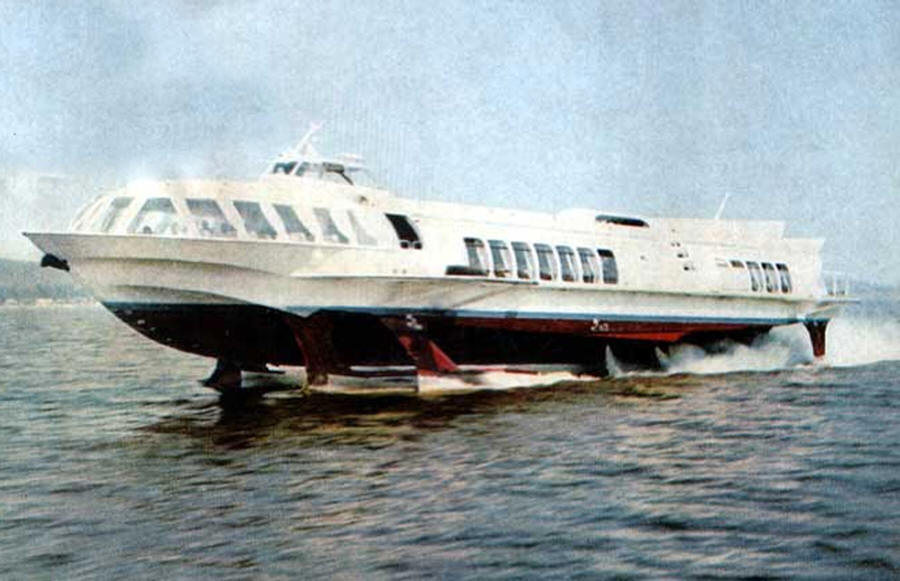

The motor ship "Meteor" was intended for high-speed river passenger transportation on suburban and local lines with a length of up to 600 km. Length - 34.6 m. Width - 9.5 m. Draft afloat - 2.3 m. Draft during the course on the wings - 1.2 m. Speed - 65 km / h. Power plant - 2x850 hp. Passengers - 124 people. "Meteors" were produced from 1961 to 1991 at the Zelenodolsk Gorky Shipyard. In total, more than 400 ships of this series were built. In the Nizhny Novgorod design bureau for hydrofoils named after Rostislav Alekseev, a Meteor-2000 modification was developed with imported engines and air conditioners, which was also supplied to China. By 2007, the Meteor production line at the plant was dismantled.
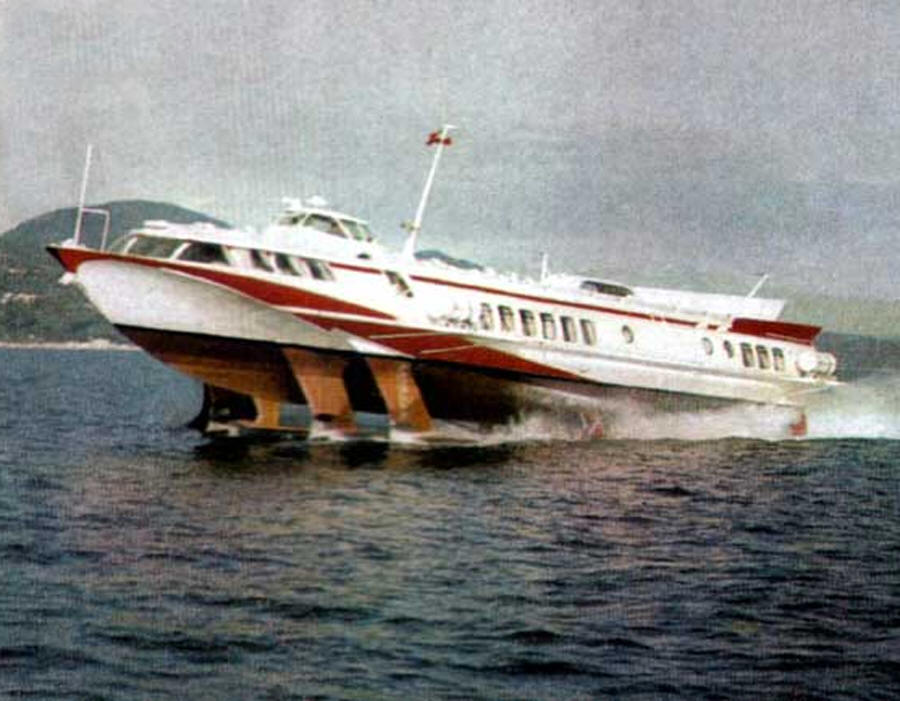

The motor ship "Kometa" was designed for high-speed passenger transportation on coastal sea lines up to 230 miles long. Length - 35.1 m. Width - 9.6 m. Draft afloat - 3.2 m. Draft during the course on the wings - 1.45 m. Speed - 32 - 34 knots. Power plant - 2x850 hp. Passengers - 118 people.
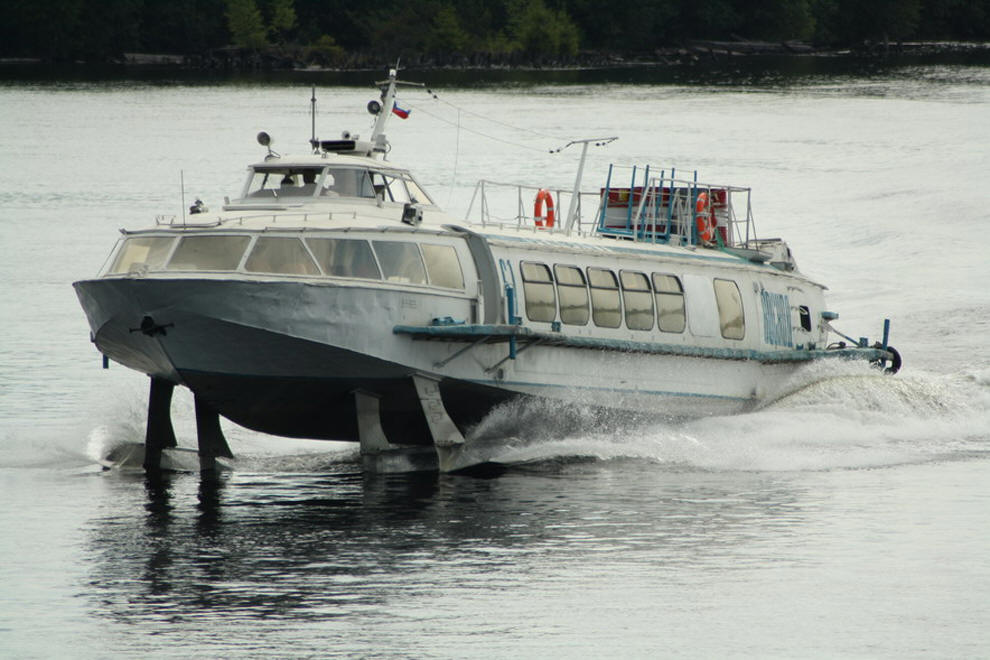

Motor ship "Voskhod" was created to replace older hydrofoils - "Rocket" and "Meteors". Length - 27.6 m. Width - 6.4 m. Draft afloat - 2.1 m. Draft during the course on the wings - 1.1 m. Speed - 65 km / h. Power plant - 2x500 hp. Passengers - 71 people. The Voskhods were built at the More shipyard in Feodosia. High-speed diesel engines for the ship were supplied by the Leningrad plant "Zvezda" and the plant "Barnaultransmash". In total, by the beginning of the nineties, more than 150 Voskhods had been built. In the nineties, the production of Voskhod practically stopped due to the difficult situation of the manufacturing plant.

The Burevestnik gas turbine vehicle is designed for high-speed passenger transportation on transit and local lines of rivers and reservoirs up to 500 km long. Length - 43.2 m. Width - 7.4 m. Draft afloat - 2.0 m. Draft when sailing on wings - 0.6 m. Speed - 90 km / h. Power - 2x2700 hp. Passengers - 150 people. "Petrel" was the flagship among the river SPK. It had a power plant based on two gas turbine engines (GTE) AI-20 designed by A. G. Ivchenko, borrowed from the Il-18 aircraft. "Petrel" existed in a single copy. It was operated from 1964 until the end of the 70s on the Volga on the route Kuibyshev - Ulyanovsk - Kazan - Gorky.
Surely, many readers still remember those glorious times when "Rockets", "Comets", "Sunrise" and "Meteors" plowed the leading water arteries of the USSR, allowing you to get from Yaroslavl to Samara, or from Yalta to Sochi in a few hours. Back in 1990, the interval for the movement of ships along the Volga was about 15 minutes, which, of course, was very convenient. In the mid-90s, "Rockets" began to disappear - they turned out to be too unprofitable for operation in a market economy. But the need for ships has not disappeared, and today the country's river fleet needs hydrofoils like air.
"Rockets" glorified Russia
Domestic shipbuilders were rightfully proud of hydrofoil passenger ships. The lead ship of the "Rocket" project, built at the "Krasnoye Sormovo" shipyard, entered service in 1957. Just in time for the international festival of youth and students in Moscow, presenting to the world the brilliant developments of Soviet scientists. From 1959 to 1976, the mass production of the "Rocket" took place at the Feodosia shipyard "More". Over the years, about 400 ships have been built. They were replaced by "Meteors" - more comfortable and meeting the requirements of the time of the court. For operation on the Black Sea, since 1960, "Comets" were built - ships designed to work in conditions of stronger waves. It was the era of space exploration, faith in scientific and technological progress and the triumph of socialist ideas. "Rockets" quickly became mega-popular, their name became a household name and often all ships of this type were called "Rockets". A trip on such a boat through picturesque places was a favorite and relatively cheap type of family vacation. Soviet man. And just a great opportunity in a matter of hours to overcome long distances in their native country.
Rebirth of a legend
Alas, in the "dashing nineties" the construction of such motor ships ceased, since they turned out to be unprofitable in a market economy. Today, there are almost no high-speed boats on Russian rivers. There are two Meteors serving the suburban line around Yaroslavl, several restored Rockets and Voskhods on the Moskva River, and several more Meteors operating sightseeing flights from St. Petersburg to Peterhof. Otherwise, the river ships operating in our time on passenger lines are too slow, their speed does not exceed 25 km / h. According to experts, given the price of fuel and routes on Russian rivers, in order for the ship to be modern and cost-effective, a completely new type is needed, capable of accelerating to 40 km / h at least. And the new-generation cruise missiles are ideal for filling this niche.
A few years ago, a competition was held at the state level for the development of new models of hydrofoils capable of becoming worthy successors of the glorious traditions of domestic shipbuilding. The winner of the competition was named the project of the Central Design Bureau. Krylov (Nizhny Novgorod). The Valdai 45 prototype is a high-speed vessel with a carbon-fiber hull 21 meters long, accommodating up to forty-five passengers and capable of speeds up to 60 km/h. And no matter how much the spiteful critics slander, but, having passed all the necessary tests, the ship was put into mass production. Considering that the Nizhny Novgorod shipyards are capable of producing several motor ships per month, very soon about five thousand Valdaevs will operate on the country's water lines.


